Breaking It Down: What You Need to Know about FDA’s Blueprint for the Future
Breaking It Down: What You Need to Know about FDA’s Blueprint for the Future
New Era of Smarter Food Safety – FDA’s Blueprint for the Future
In July 2020, the FDA released their 10-year approach for enhancing the safety of the nation’s food supply through the “New Era of Smarter Food Safety: FDA’s Blueprint for the Future”. The ultimate goal of the Blueprint is to ‘bend the curve’ of food-borne illnesses in the U.S. by focusing on four core elements. Below, we break down the key points for each element:

Tech-enabled Traceability
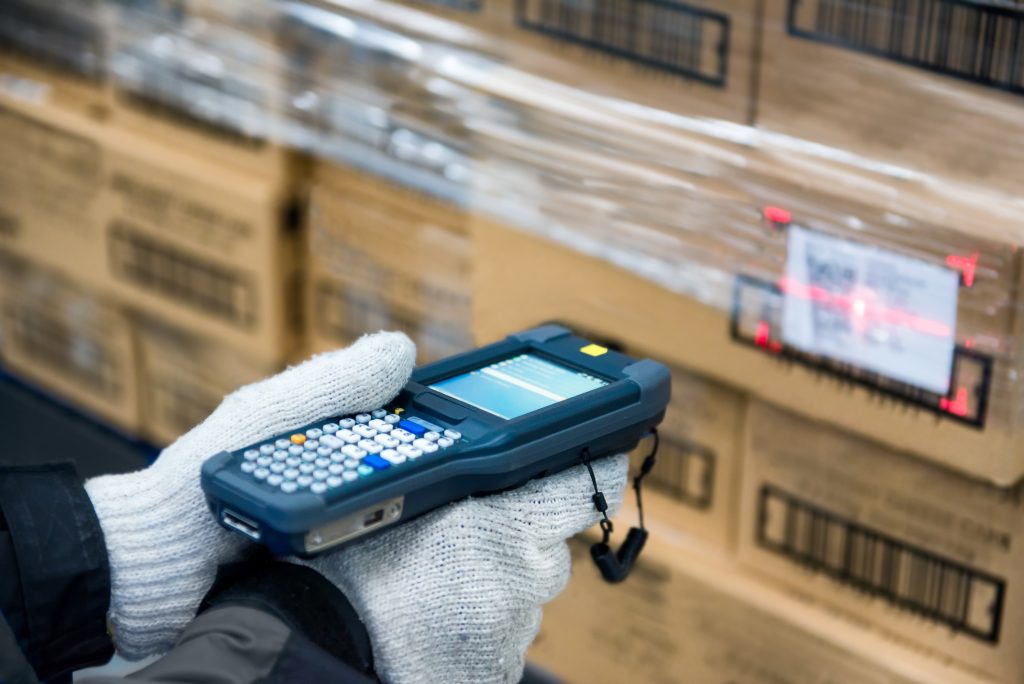
Technology-enabled traceability offers rapid tracebacks of contaminated products and more efficient removal of adulterated products from the marketplace. The FDA’s first step towards tech-enabled traceability is the finalization of FSMA Section 204 rule-making, which standardizes the key data elements and critical tracking events of traceability. The proposed rule harmonizes the traceability language used across the industry and also creates additional record keeping requirements for high-risk foods. To promote tech-enabled traceability, the FDA plans to engage in conversations with non-traditional stakeholders (i.e., insurance companies) for opportunities to incentivize companies to adopt new technologies, as well as taking traceability into account in risk-based planning for inspections.
Smarter Tools and Approaches for Prevention and Outbreak Response
The FDA plans to strengthen outbreak root cause analyses by collaborating with state, local, and other federal partners to ensure the rapid deployment and optimization of resources when an outbreak site is identified, and to enhance communication tools for relaying the outcomes of the analyses. Additionally, the FDA will expand its use of artificial intelligence and machine learning tools to advance predictive analytics capabilities. Root cause analysis data and predictive analytical systems will be used in risk ranking and planning for inspections.
New Business Models and Retail Modernization
The use of online grocery shopping and food delivery services surged as consumers adapted to the situations created by the COVID-19 pandemic. The FDA plans to address food safety concerns with these emerging business models by educating both consumers and food delivery companies on the importance of proper handling of food delivered to homes. Additionally, the FDA plans to increase uniform adoption of the FDA Food Code by state and local retail food protection programs. The FDA will also continue to focus on food safety in traditional retail establishments.
Food Safety Culture
The FDA will encourage food-safe behaviors throughout the food system. This includes farmers/growers, social media influencers, and consumers, making food safety behavior the social norm. The FDA also plans to develop assessment tools for measuring food safety culture. They will evaluate how companies’ positive food safety cultures can factor into reduced inspection frequencies.
Is Your Company Ready for the FDA’s Initiatives?
Consider the following actions to best prepare your operation:
- Establishments that Manufacture, Pack, or Hold High-risk Foods (i.e., soft cheeses, leafy greens, fruit-cut fruits/vegetables, RTE deli salads):
- Evaluate your traceability system against the requirements of FSMA Section 204.
- Establish and maintain records containing Key Data Elements (KDEs) associated with Critical Tracking Events (CTEs).
- E-commerce or Food Delivery Businesses:
- Assess your operation for food safety risks, such as temperature control, cross-contamination, and tamper-resistance.
- Evaluate methods for monitoring time, temperature, and traceability.
- Retail Establishments:
- Assess your operation for best practices in food safety, using the 2017 FDA Food Code to evaluate compliance.
- All Operations:
- Develop or strengthen a food safety culture across your organization!
- Conduct a food safety culture gap assessment to identify areas of opportunities within your establishment.
- If you do not already have a connection with a Food Safety Professional, begin researching possible connections today.